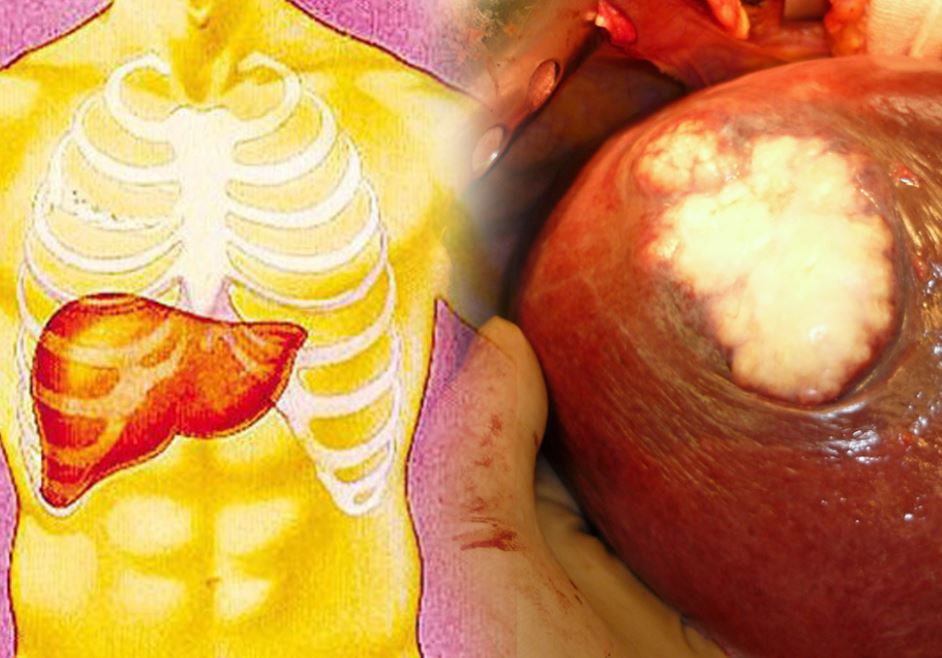
Liver cancer, also known as hepatocellular carcinoma, is a type of cancer that starts in the cells of the liver. It is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt medical attention and treatment. If caught early, liver cancer can often be treated successfully. Here are some options for treating liver cancer
Treatment Options for Liver Cancer
Surgery
Surgery is often the first option for treating liver cancer. The type of surgery used will depend on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the overall health of the patient.
- Partial hepatectomy: This procedure involves removing the portion of the liver that contains the tumor, as well as a margin of healthy tissue around it. It is often possible to remove the entire tumor with this procedure.
- Liver transplant: In some cases, a liver transplant may be an option. This procedure involves removing the entire liver and replacing it with a healthy liver from a donor. A liver transplant is typically only considered for patients with small, early-stage tumors and no evidence of cancer spread to other parts of the body.
- Radiofrequency ablation: This procedure involves using heat to destroy cancer cells. It is usually only used for small, early-stage tumors that are not suitable for surgery.
Ablation and Embolization Procedures
Ablation and embolization procedures involve destroying or blocking the blood supply to the cancer cells. These procedures can be used to shrink or slow the growth of liver tumors.
- Radiofrequency ablation: This procedure uses heat to destroy cancer cells. It is typically performed using a needle that is inserted through the skin into the tumor.
- Cryoablation: This procedure uses extreme cold to destroy cancer cells. It is typically performed using a probe that is inserted through the skin into the tumor.
- Embolization: This procedure involves blocking the blood supply to the cancer cells. It is typically performed using a catheter that is inserted through an artery in the leg and guided to the liver.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that targets specific molecules or pathways involved in cancer cell growth and survival. It can be used to slow the growth of liver cancer or shrink tumors.
- Sorafenib (Nexavar): This drug targets certain proteins that are involved in cancer cell growth and survival. It is typically used to treat advanced liver cancer that cannot be removed with surgery.
- Lenvatinib (Lenvima): This drug targets certain proteins that are involved in cancer cell growth and survival. It is typically used to treat advanced liver cancer that cannot be removed with surgery.
- Regorafenib (Stivarga): This drug targets certain proteins that are involved in cancer cell growth and survival. It is typically used to treat advanced liver cancer that cannot be removed with surgery.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a treatment option for liver cancer that involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. There are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used to treat liver cancer, including:
- Doxorubicin (Adriamycin): This drug is a type of anthracycline antibiotic that interferes with the cancer cells’ ability to divide and grow. It is typically administered intravenously and may be used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs. Common side effects of doxorubicin include nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and fatigue.
- Fluorouracil (5-FU): This drug is a type of antimetabolite that interferes with the cancer cells’ ability to divide and grow. It is typically administered intravenously or by injection and may be used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs. Common side effects of fluorouracil include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and low white blood cell count.
- Gemcitabine (Gemzar): This drug is a type of nucleoside analogue that interferes with the cancer cells’ ability to divide and grow. It is typically administered intravenously and may be used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs. Common side effects of gemcitabine include nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and low white blood cell count.
